"Tissues" PART-1 (Plant Tissues)
TISSUES PART 1 (PLANTS TISSUES)
Notes by:- Nagraj Sir
Tissue: A group of cells, that are
similar in structure and work together to achieve a particular function, forms
a tissue. they are two types
1-meristematic
2-Permanent
Meristematic tissue: Meristematic tissues are the tissues which have the ability to grow by rapid division. They help in the primary growth of the plant. These cells are closely packed with no intercellular spaces. they are 3 types
Meristematic tissue: Meristematic tissues are the tissues which have the ability to grow by rapid division. They help in the primary growth of the plant. These cells are closely packed with no intercellular spaces. they are 3 types
1-APICAL
2-LATERAL
3- INTERCALARY
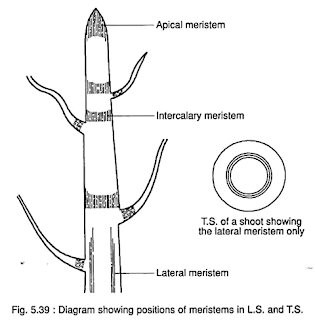
• Apical meristem is present at the apical or growing tips of stems and roots. Apical meristem increases the length of the plant.
• Lateral meristem is present in the radial portion of the stem or root. Lateral meristem increases the girth of the plant.
• Intercalary meristem occurs at the base of the leaves or at the internodes. Intercalary meristem increases the length of the internode.
• Apical meristem is present at the apical or growing tips of stems and roots. Apical meristem increases the length of the plant.
• Lateral meristem is present in the radial portion of the stem or root. Lateral meristem increases the girth of the plant.
• Intercalary meristem occurs at the base of the leaves or at the internodes. Intercalary meristem increases the length of the internode.
Permanent tissues: The cells which have lost their capacity to divide but are specified to provide strength, flexibility and elasticity to the plant.
They are 2 types:-
1.SIMPLE PERMANENT TISSUE
2.COMPLEX
PERMANENT TISSUE
• SIMPLE PERMANENT TISSUE :- 3 types:-
• SIMPLE PERMANENT TISSUE :- 3 types:-
1.PARENCHYMA
2.COLLENCHYMA
3.SCLERENCHYMA
PARENCHYMA – These are living, polygonal, oval, spherical cells with a large central vacuole, and have large intercellular spaces between them. Cell wall in thin and made up of cellulose
• Parenchyma containing chloroplasts are called chlorenchyma. The chlorenchyma help in photosynthesis.
• Parenchyma which contain large air cavities are called aerenchyma. The aerenchyma help in buoyancy to plant to float on water.
• Some parenchymatous cells act as storage cells for starch in fruits and vegetables.
COLLENCHYMA – These are elongated living cells with small intercellular spaces or some time absent. Their cell walls are made up of cellulose and pectin. Collenchyma occur in the peripheral regions of stems and leaves to provide mechanical support and flexibility in plants.
SCLERENCHYMA – These are long, dead cells with a deposit of lignin in their cell wall. They have no intercellular spaces. Sclerenchyma occur around the vascular tissues in stems, in the veins of leaves, and in the covering of seeds and nuts husk of coconut. They provide mechanical strength to the plant and provide protection against external environment factor.
•
COMPLEX PERMANENT TISSUE :- Two Types
1-XYLEM
2-PHLOEM
XYLEM – This tissue helps in the transport of water and dissolved substances throughout the plant. The 4 different components of the xylem include tracheids, vessels, xylem parenchyma and xylem fibres. Tracheids and xylem fibres are made up of lignin, which provides mechanical support to the plant.
PHLOEM – This tissue helps in the transport of food throughout the plant. The 4 different elements of phloem include sieve tubes, companion cells, phloem parenchyma and phloem fibres.
XYLEM – This tissue helps in the transport of water and dissolved substances throughout the plant. The 4 different components of the xylem include tracheids, vessels, xylem parenchyma and xylem fibres. Tracheids and xylem fibres are made up of lignin, which provides mechanical support to the plant.
PHLOEM – This tissue helps in the transport of food throughout the plant. The 4 different elements of phloem include sieve tubes, companion cells, phloem parenchyma and phloem fibres.
Important terms:-
Epidermis – A layer of cells making up an outer covering of all the structures in the plant. The layer epidermis is perforated by the stomata at certain places. The stomata help in gaseous exchange and loss of water.
Cork – This is the outer protective tissue which replaces the epidermal cells in older roots and stems. Cork cells are dead and lack intercellular spaces. Their cell walls are thickened by suberin which makes them impermeable to water and gas molecules.

Thank sir
ReplyDeleteThankyou sir
ReplyDeleteThanky so much sir
ReplyDeleteThank you much sir
ReplyDeleteThank you much sir
ReplyDelete